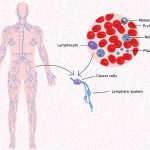
Breast cancer occurs when healthy cells in the breast change and grow out of control, forming a mass known as a tumor. A malignant tumor can grow and spread to other parts of the body. When breast cancer spreads beyond the breast to other organs, it is known as metastatic breast cancer or stage 4 breast cancer. This advanced stage indicates that cancer has moved to areas like the liver, bones, lungs, or brain.
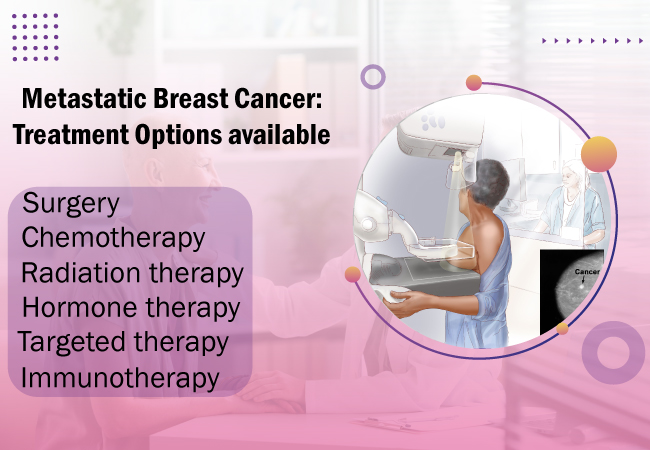
Treatment Options for Metastatic Breast Cancer:
Metastatic breast cancer requires a comprehensive approach. Treatments are aimed at slowing the spread, controlling symptoms, and improving quality of life. Here are the main treatment options:
Surgery: In metastatic breast cancer, surgery is less common but may be used to remove isolated tumors or relieve symptoms. The main types of breast cancer surgeries include:
- Breast-conserving surgery: Removes only the cancerous tissue.
- Mastectomy: Removes the entire breast to prevent further spread.
- Modified radical mastectomy: Removes the entire breast, including some lymph nodes.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy involves using drugs to kill or stop the growth of cancer cells. It is usually administered when cancer has spread to multiple parts of the body. Below are the FDA-approved chemotherapy drugs for metastatic breast cancer:
- Capecitabine (Xeloda)
- Paclitaxel (Taxol)
- Docetaxel (Taxotere)
- Doxorubicin (Adriamycin)
- Epirubicin (Ellence)
- Cisplatin (Platinol)
- Cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan)
- Carboplatin (Paraplatin)
- Vinorelbine (Navelbine)
- Gemcitabine (Gemzar)
- Eribulin (Halaven)
Hormone Therapy: Hormone therapy is used for hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer. It blocks or lowers the hormones that fuel cancer growth. The following are FDA-approved hormone therapies for metastatic breast cancer:
- Tamoxifen (Nolvadex): A selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) used for both pre-and post-menopausal women.
- Anastrozole (Arimidex): An aromatase inhibitor for postmenopausal women.
- Letrozole (Femara): Another aromatase inhibitor used to reduce estrogen levels.
- Exemestane (Aromasin): An aromatase inhibitor prescribed for postmenopausal women.
- Fulvestrant (Faslodex): An estrogen receptor antagonist, often used after other hormone therapies.
- Goserelin (Zoladex): Used in premenopausal women to suppress ovarian function.
Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapies are designed to attack specific proteins or genes that contribute to cancer growth. Below are FDA-approved targeted therapies for metastatic breast cancer (as of October 2024):
- Trastuzumab (Herceptin): A monoclonal antibody targeting HER2-positive breast cancer.
- Pertuzumab (Perjeta): Often used in combination with trastuzumab for HER2-positive cancers.
- Ado-trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla): Combines trastuzumab with chemotherapy.
- Trastuzumab deruxtecan (Enhertu): Approved for HER2-positive cancers that have metastasized.
- Lapatinib (Tykerb): A tyrosine kinase inhibitor used in HER2-positive cancers.
- Neratinib (Nerlynx): Used after trastuzumab-based therapy for extended treatment.
- Palbociclib (Ibrance): A CDK4/6 inhibitor used in hormone receptor-positive cancers.
- Ribociclib (Kisqali): Another CDK4/6 inhibitor for HR+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer.
- Abemaciclib (Verzenio): A CDK4/6 inhibitor used either alone or with hormone therapy.
- Everolimus (Afinitor): An mTOR inhibitor used in combination with hormone therapy.
- Alpelisib (Piqray): A PI3K inhibitor used with fulvestrant for PIK3CA-mutated cancers.
- Olaparib (Lynparza): A PARP inhibitor for BRCA-mutated cancers.
- Talazoparib (Talzenna): Another PARP inhibitor for patients with BRCA mutations.
- Sacituzumab govitecan (Trodelvy): Approved for triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) that has spread.
Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy helps the body’s immune system fight cancer. The following are FDA-approved immunotherapy drugs for metastatic breast cancer (as of October 2024):
- Pembrolizumab (Keytruda): A PD-1 inhibitor used in combination with chemotherapy for PD-L1-positive TNBC.
- Atezolizumab (Tecentriq): Another PD-L1 inhibitor used for metastatic TNBC.
Current Statistics and Data:
In India, breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women. According to the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), approximately 30% of all breast cancer cases in the country are diagnosed at the metastatic stage. Recent advances in treatment have significantly improved outcomes for many women. The availability of targeted therapies, hormone therapies, and immunotherapies in India has improved survival rates, allowing many patients to live longer and with better quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What are the symptoms of metastatic breast cancer?
Common symptoms include bone pain, difficulty breathing, persistent cough, headaches, or unexplained weight loss. The symptoms depend on where the cancer has spread.
Can metastatic breast cancer be cured?
Metastatic breast cancer is not curable, but treatments can control the disease and help manage symptoms. Many patients live longer with the right therapies.
How long can someone live with metastatic breast cancer?
Survival rates vary based on factors like the spread of the disease and how well the treatment works. However, advancements in treatment are allowing many patients to live for several years after diagnosis.
What is the best treatment for metastatic breast cancer?
The best treatment depends on the type of cancer (HER2-positive, hormone receptor-positive, or triple-negative) and where it has spread. Treatment typically includes a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.
Are these advanced treatments available in India?
Yes, many of these FDA-approved treatments, including targeted therapies and immunotherapies, are available in India, improving survival rates for patients with metastatic breast cancer.
How can I buy breast cancer medicines in India?
To buy breast cancer medicines such as Capecitabine (Xeloda), Paclitaxel (Taxol), Docetaxel (Taxotere), Doxorubicin (Adriamycin), Epirubicin (Ellence), Cisplatin (Platinol), Cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan), Carboplatin (Paraplatin), Vinorelbine (Navelbine), Gemcitabine (Gemzar), Eribulin (Halaven), Trastuzumab (Herceptin), Pertuzumab (Perjeta), Lapatinib (Tykerb), Neratinib (Nerlynx), Palbociclib (Ibrance), Ribociclib (Kisqali), Everolimus (Afinitor), Alpelisib (Piqray), Olaparib (Lynparza), or Atezolizumab (Tecentriq), please contact Indian Pharma Network (IPN) via Call/WhatsApp: +91 9310090915 or TOLL-FREE: 1800-889-1064. We help facilitate the legal supply of these therapeutic drugs in India and other countries