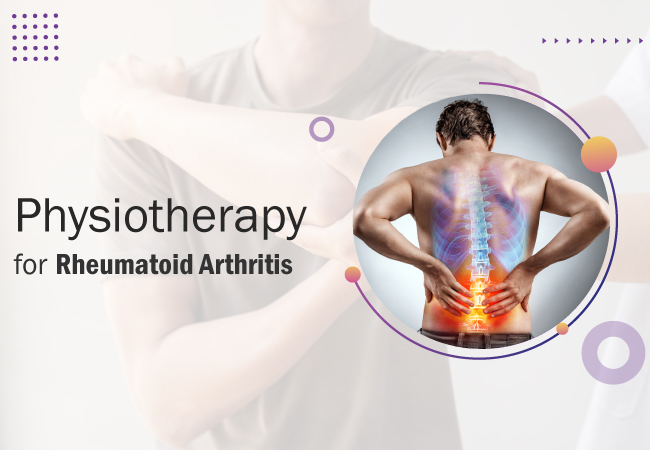
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is more than just a chronic condition; it’s a journey through pain, joint damage, and reduced quality of life. This autoimmune disease occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, leading to debilitating symptoms. The causes of RA remain somewhat of a mystery, but several factors can contribute to its development, including age, gender, genetics, smoking, diet, and body weight.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis:
Rheumatoid arthritis is often characterized by its impact on joints, especially the small ones in the hands and feet. Patients frequently experience:
- Swelling and Pain: Joints may feel tender and warm, often swelling in response to inflammation.
- Stiffness: Particularly noticeable in the morning, stiffness can last for over 30 minutes and sometimes several hours.
- Grip Weakness: Difficulty in holding objects firmly is common.
Unlike osteoarthritis, which typically occurs with age, RA can affect individuals at any age and can coexist with osteoarthritis.
The Role of Physiotherapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis:
Physiotherapy is an essential component in managing rheumatoid arthritis. The primary goals of physiotherapy are to:
- Prevent Disability: Help patients maintain their independence and ability to perform daily activities.
- Enhance Functional Capacity: Improve movement and flexibility to aid in daily life.
- Provide Pain Relief: Utilize various techniques to alleviate pain.
- Educate Patients: Teach coping strategies and exercises to manage symptoms.
Before starting therapy, physiotherapists assess the individual needs of patients based on their specific challenges and limitations.
Key Physiotherapy Techniques for Rheumatoid Arthritis:
Cold and Hot Applications:
- Cold Therapy: Best for acute flare-ups, cold packs can reduce inflammation and numb sharp pain.
- Heat Therapy: Beneficial during chronic phases, heat can relieve muscle spasms and improve circulation. It’s best to apply heat before engaging in exercises for optimal results.
Electrical Stimulation:
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): A popular method to relieve pain, TENS involves applying electrical currents to affected areas. Studies suggest that regular use can improve hand grip strength and decrease pain levels significantly
- Hydrotherapy: Also known as balneotherapy, hydrotherapy involves using water for therapeutic purposes. Historically, patients with rheumatic diseases have sought relief through water-based treatments. The goals of hydrotherapy include increasing the range of motion, reducing muscle spasms, and enhancing overall well-being.
- Exercise Programs: Proper exercise routines, focusing on low-impact activities, can strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce joint stiffness. Programs may include stretching, strengthening, and aerobic exercises, all designed to suit individual needs.
- Patient Education: Empowering patients with knowledge about their condition and self-management techniques plays a crucial role in their treatment journey. Learning about joint protection, energy conservation, and the importance of adhering to therapy can make a significant difference.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What are the early signs of rheumatoid arthritis?
Early signs include joint swelling, morning stiffness lasting over 30 minutes, and persistent fatigue. If you notice these symptoms, consult a healthcare professional promptly.
Can physiotherapy help with rheumatoid arthritis?
Yes, physiotherapy is instrumental in managing rheumatoid arthritis. It helps improve joint function, reduce pain, and enhance your overall quality of life through various therapeutic techniques.
Is exercise safe for someone with rheumatoid arthritis?
Absolutely! Engaging in gentle, low-impact exercises is beneficial. A physiotherapist can help design a program that considers your abilities and limitations, ensuring safe and effective workouts.
How often should I see a physiotherapist for rheumatoid arthritis?
The frequency of visits depends on your specific condition and treatment plan. Initially, you may visit once or twice a week, then transition to a maintenance schedule as you improve.
Is there a new medicine for rheumatoid arthritis approved by the FDA?
Yes, Kineret (anakinra) is a newer medication approved by the FDA for rheumatoid arthritis. It works by blocking interleukin-1, reducing inflammation and pain, and offering patients an additional treatment option for managing their symptoms effectively.
Are there any lifestyle changes I can make to help manage rheumatoid arthritis?
Yes, maintaining a balanced diet, quitting smoking, staying active, managing weight, and reducing stress can all positively impact your symptoms. It’s essential to adopt a holistic approach to manage your health effectively.
Conclusion:
Living with rheumatoid arthritis doesn’t mean surrendering to pain and limitations. With the right physiotherapy approach, you can reclaim your life. By incorporating a blend of techniques tailored to your needs, physiotherapy can help you navigate this journey with hope and resilience. Embrace the support available to you, and take proactive steps toward a more vibrant and fulfilling life.
References:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1395797/
https://www.physio.co.uk/what-we-treat/rheumatology/rheumatoid-arthritis.php